Prototype is an important concept in the Javascript programming language, especially when building and maintaining source code. In this article, we will learn about the concept of Prototype, how it works and specific instructions on how to set up Prototype in Javascript.
Introduction to Prototype
What is Prototype?
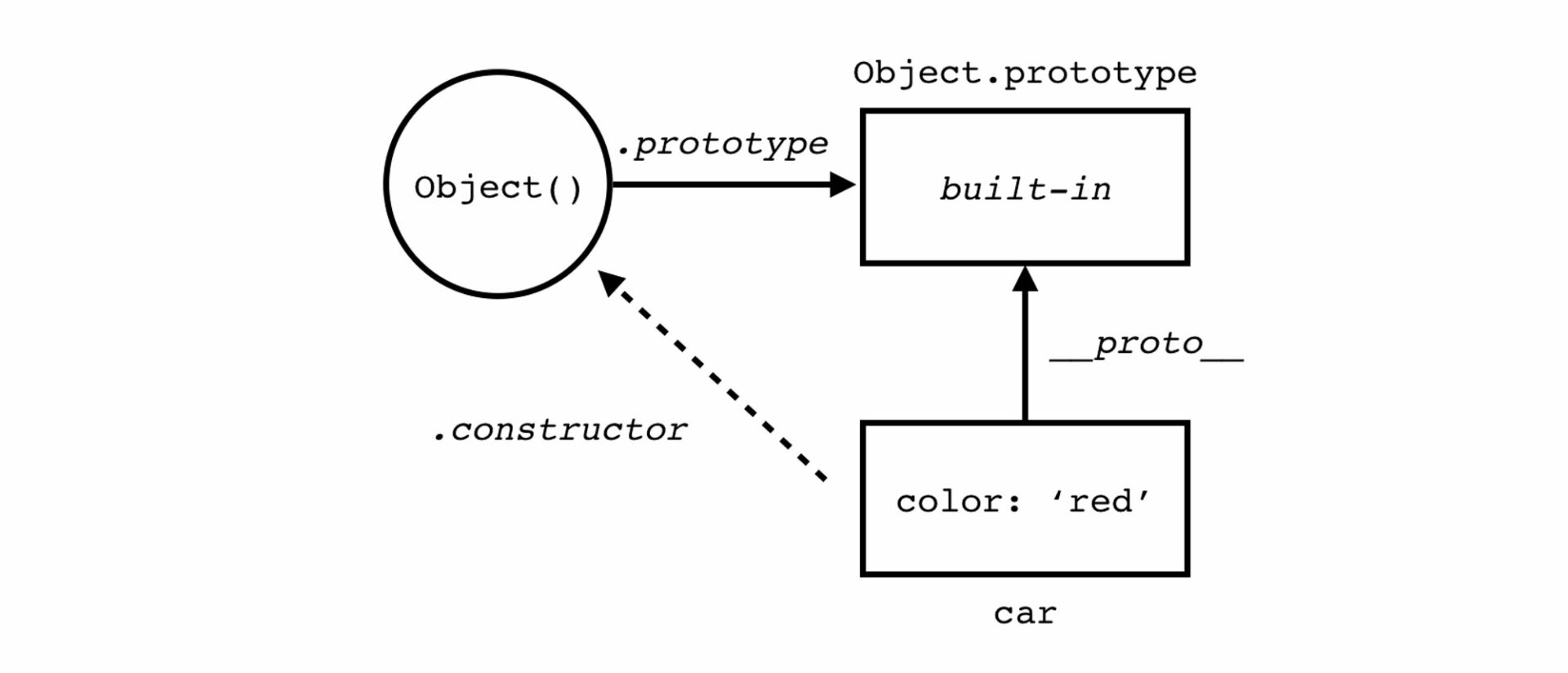
Prototype is a mechanism for implementing Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in the JavaScript programming language, where objects inherit features from each other. In JavaScript, every object has an internal property called a prototype. This language automatically links to every function and object by default, where the prototype property of a function can be accessed and modified. In contrast, the prototype property of an object remains hidden. A prototype is a special type of object that can attach additional properties, and this object will be shared across all instances of the initializing function.
Benefits of Using Prototype
Prototype brings numerous benefits to JavaScript programming, including:
Code Reusability
Prototype allows you to share common properties and methods among objects, reducing code repetition and optimizing efficiency.
Instead of writing code for each object separately, you only need to define properties and methods in the Prototype once, saving time and effort.
Inheritance
Prototype serves as the foundation for inheritance in JavaScript, helping you build complex code structures and manage them effortlessly.
Child objects can inherit properties and methods from parent objects, minimizing code size and increasing scalability.
Flexibility
Prototype allows you to add properties and methods to already created objects, providing flexibility in the programming process.
You can easily update and expand the functionality of objects without having to recreate them.
Efficiency
Using Prototype helps optimize performance, as instances do not need to store copies of inherited properties and methods.
This minimizes memory usage and accelerates the application’s processing speed.
Maintainability
Prototype makes JavaScript code more readable and understandable, contributing to improved maintainability.
Sharing common properties and methods makes it easy to manage and update the code.
Detailed Guide on Setting Up Prototype
There are two common ways to set up a prototype for an object in JavaScript: using Object.create() and constructor functions.
Using Object.create()
One popular method for setting up a prototype is using the Object.create() method. It is a flexible way to create a new object and specify its prototype. Here is an illustrative example:
const personPrototype = {
greet() {
console.log('hello!');
}
}
const carl = Object.create(personPrototype);
carl.greet(); // hello!Using Constructor Functions
Another way to set up a prototype is by using constructor functions. When an object is created using the new keyword, its prototype is linked to the prototype of the object’s constructor function. Here’s an example:
const personPrototype = {
greet() {
console.log(`hello, my name is ${this.name}!`);
}
}
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype = personPrototype;
Person.prototype.constructor = Person;Using Prototype in JavaScript
This language enables users to easily define methods for all instances of an object. The beauty lies in applying the method to the prototype, as it is stored in memory only once. However, every instance of the object has access to it.
Example:
function Pet(name, species){
this.name = name;
this.species = species;
}
function view(){
return this.name + " is a " + this.species + "!";
}
Pet.prototype.view = view;
var pet1 = new Pet('Gabriella', 'Dog');
alert(pet1.view()); //Outputs "Gabriella is a Dog!"In this function, simply by using the prototype when attaching the view method, we ensure that all Pet objects have access to the view method. Additionally, the prototype method can be used to create more effects.
Example:
function Pet(name, species){
this.name = name;
this.species = species;
}
function view(){
return this.name + " is a " + this.species + "!";
}
Pet.prototype.view = view;
function Dog(name){
Pet.call(this, name, "dog");
}
Dog.prototype = new Pet();
Dog.prototype.bark = function(){
alert("Woof!");
}In this function, we set up the Dog object and call the Pet function using the call() method. The call() method allows calling a specific target function inside an object by passing the object to be referenced by ‘this’ at line 10, followed by the arguments. Then, we give the Dog object a method called bark (only Dog objects have access to it).
var pet1 = new Pet('Trudy', 'Bird');
var pet2 = new Dog('Gabriella');
alert(pet2.view()); // Outputs "Gabriella is a Dog!"
pet2.bark(); // Outputs "Woof!"
pet1.bark(); // ErrorThis way, we have set up the Dog object, and by calling the Pet function, we have made Pet inherit Object.prototype.
Object.prototype.whoAmI = function(){
alert("I am an object!");
}
pet1.whoAmI(); //Outputs 'I am an object!'
pet2.whoAmI(); //Outputs 'I am an object!'
This language works in a chain. When calling pet2.view(), it must first check whether the Dog and Pet objects have the view method. Since Dog inherits Pet, and Pet inherits Object.prototype, the Object.prototype.whoAmI() method is applied.
Buying Cheap Proxies at proxyv6.net
Buying cheap proxies at proxyv6.net is a smart decision for those who need to use proxies to improve performance and protect online privacy. Proxyv6.net provides quality proxy services with various types of proxies, from HTTP and HTTPS to SOCKS, catering to diverse user needs. Using proxies not only helps anonymize personal information but also enhances safety when browsing the web and performing online activities. Particularly, proxyv6.net offers cheap proxy packages suitable for individual users to businesses. Furthermore, applying the prototype concept in the JavaScript programming language allows users to leverage the flexibility of the prototype to create and manage objects efficiently. The combination of buying cheap proxies at proxyv6.net and implementing the prototype in JavaScript programming can provide users with powerful and secure online experiences.